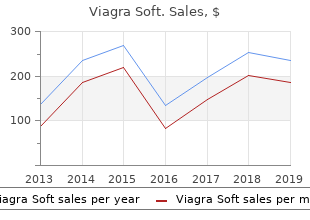
Viagra Soft
Louisiana State University at Baton Rouge. G. Gelford, MD: "Purchase online Viagra Soft no RX. Cheap Viagra Soft.".
A regional stakeholder 52 NIHR Journals Library www order viagra soft 50 mg on-line erectile dysfunction herbs. That aspect has arguably been party addressed by the STP initiative buy 50mg viagra soft with visa erectile dysfunction prevalence age. The need for such changes were being identified by the actors in this case cheap viagra soft line erectile dysfunction icd 0. There is a lot of support for MCPs in the system whereas people often feel quite threatened by the PACS model generic viagra soft 100 mg with mastercard erectile dysfunction doctors huntsville al. The initiative to generate primary care provider organisations is sensible. However, it is worth noting that the PACS model, with a hospital base, has the advantage of a better resourced and professional management structure and capability. Secondary care clinical lead The new models of care were generally welcomed by all those whom we interviewed. They were regarded as mechanisms which could help resolve many of the issues associated with the CCG initiatives taken to date as discussed earlier. The level 3 element of the programme, which involved innovations which could transfer appropriate services from hospitals to primary care, was recognised as precarious. Where clinicians talked to clinicians (GPs to consultants), it was argued that they could often identify areas of agreement about which services could be transferred. The consultants were pleased to be rid of much of the high-volume routine work. However, there was the question of the implications on the income flow into the hospitals and the means by which funds would be transferred to match changes in activity. The finance managers were cautious but, given the penalties imposed for breaches of performance targets, they too could be persuaded to relinquish some of this kind of work. At the time of our research at this site there was huge uncertainty whether or not the corresponding alterations to activity in the acute sector were happening. There was no doubt, however, that general practice across the CCG had been improved even though there was more to do. A few general practices decided to transfer to a neighbouring CCG in order to avoid the change programme. Summary: clinical leadership across different arenas Clinical leadership was present in this case in the form of a determined push by a close group of three GPs at the summit of the CCG to reform primary care as a whole and general practice in particular. This leadership was enacted in all three arenas outlined in the analytical framework presented at the start of this chapter (see The analytical framework and Figure 24). The strategic planning was undertaken in the arena of the CCG central governing body. The operational activity was undertaken in the programme board for primary care and in the locality groups. The third arena for institutional work was at the practice level; here, the distributed clinical leadership was of a more variable nature and some GP practices moved ahead in delivering the primary care improvement programme much more fully and rapidly than others. Notably, the kind of institutional work being undertaken by the leaders in this CCG was bounded by the institutional reach which they judged they could attain. They challenged existing practices, prescribed new versions of acceptable practice and set new levels of attainment. This required a complex mix of joint problem identification, joint problem-solving, visioning, contingent reward and, ultimately, prescription and monitoring.
In order to answer these questions order viagra soft with visa impotence due to diabetes, the research design was built purchase viagra soft now erectile dysfunction due to diabetes, centrally generic viagra soft 50mg prices for erectile dysfunction drugs, around a study of initiatives in specific service areas in order to map these in a manner which dug beneath the rhetoric of reform purchase viagra soft 50mg on-line erectile dysfunction medication contraindications. These service areas were identified by the wide range of stakeholder informants at the scoping stage as the ones most critical to the future viability of the NHS. The service areas identified were redesigning urgent care, managing long-term conditions, care of the frail elderly and mental health. Our central concern was how clinicians used, and were affected by, the institutional mechanisms. Lessons learned in manoeuvring through and around these carry a significance beyond the specifics of the CCG formation. A considerable amount of activity was initiated by clinical leaders who were not in a formal post within a CCG. In 2012/13, the idea of facilitating clinical leadership through localised commissioning bodies was not entirely new. Former experiments included GP fundholding and related forms. All CCGs have had to take note of, and respond in some way to, these policy thrusts. Inevitably, our research work in and around CCGs tracked these responses as they occurred in real time. During the period since their inception, there appears to have been increasing oversight and monitoring of CCGs, most especially by NHSE and the Care Quality Commission (CQC). An interesting feature here is the way local commissioners are being held to account by central agencies in addition to the accountability to the local membership. In 2017, a number of CCG mergers were approved and further mergers leading to fewer and larger CCGs are likely to follow. The requirement on local health economies to construct sustainability and transformation plans (STPs) also represents a game-changing initiative concerning the redesign of health and social care. Although the STPs require engagement by CCGs, local authorities (LAs) and provider trusts, there are concerns that these bodies, creations of the centre, may come to diminish the influence of CCGs. These profound ongoing shifts in the wider context were very much borne in mind by the members of the research team as they progressed with the task of finding answers to the original set of research questions. Research questions The overall aim was to assess and clarify the extent, nature and effectiveness of clinical engagement and leadership in the work of the CCGs. This was broken down into five main research questions. What is the range of clinical engagement and clinical leadership modes being used in CCGs? What is the extent and nature of the scope for clinical leadership and engagement in service redesign that is possible and facilitated by commissioning bodies, particularly the CCGs and the health and well-being boards (HWBs)? What is the range of benefits being targeted through different kinds of clinical engagement and leadership? What are the forces and factors that serve either to enable or block the achievement of benefits in different contexts, and how appropriate are different kinds of clinical engagement and leadership for achieving effective service design? What can be learned from international practices of clinical leadership in service redesign in complex systems that will be of theoretical and practical value to CCGs and HWBs? The case studies and the national surveys were used as means to generate relevant data to help answer these questions. Before we present the findings and our interpretations of those findings, it is necessary to: (a) summarise the state of knowledge about these questions as found in the existing literature (b) introduce the theoretical lens we used in undertaking the analysis found in later chapters (c) describe the research methods which we deployed in this study. In seeking to answer the research questions we were of course aware that there were existing literatures relevant to aspects of the research agenda, most notably literatures concerning the policy context, previous initiatives prompting GP commissioning, clinical leadership more broadly and service redesign in health.
A single time series order viagra soft with a visa erectile dysfunction symptoms, representative of this region generic viagra soft 100 mg erectile dysfunction doctor type, was defined by the first eigenvector of all the voxels in the region of interest (15) cheap 50 mg viagra soft otc erectile dysfunction doctor in pakistan. Our model of the dorsal visual stream included the lateral FIGURE 29 discount viagra soft 100 mg fast delivery impotence because of diabetes. This graph shows the correlation between the temporal index of geniculate nucleus, V1, V5, and the PP. Although connec- changes in effective connectivity and learning. The temporal tions between regions are generally reciprocal, for simplicity index is defined as the time of a maximum increase in effective we modeled only unidirectional paths. For example, a temporal index of 3 indicates To assess effective connectivity in a condition-specific that the maximum increase in effective connectivity occurred be- fashion, we used time series that comprised observations tween the third and fourth blocks. The numbers denote the sub- during the condition in question. Path coefficients for both ject from which this temporal index of effective connectivity was obtained. Each subject was scanned during three independent conditions (attention and no attention) were estimated by learning sessions; therefore, each number appears three times. To test for the im- A negative slope means that the maximum increase in effective pact of changes in effective connectivity between attention connectivity occurs earlier in fast learning. The predictive value of changes in effective connec- and no attention, we defined a free model (allowing different tivity for human learning. Science 1999;283:1538–1541, with per- path coefficients between V1 and V5 for attention and no mission. The connectivity be- tween V1 and V5 increases significantly during attention. The specific hypothesis we addressed was that parietal cortex could modulate the inputs from V1 to V5. The experiment was performed on a 2-T MRI system equipped with a head volume coil. The subject was scanned during four dif- ferent conditions: fixation, attention, no attention, and sta- tionary. Each condition lasted 32 seconds to give 10 volumes per condition. During all conditions, the subjects looked at a fixation point in the middle of a screen. In this section, we are interested only in the two conditions with visual motion (attention and no attention), in which 250 small white dots moved radially from the fixation point, in random directions, toward the border of the screen at a constant speed of 4. The difference between attention and no attention lay in the explicit command given to the subject shortly before the condition: just look indicated no attention, and FIGURE 29. Structural equation model of the dorsal visual pathway, comparing attention and no attention. Connectivity be- detect changes indicated the attention condition. Both visual tween right primary visual cortex (V1) and motion-sensitive area motion conditions were interleaved with fixation. No re- (V5) is increased during attention relative to no attention.
Te proportion of people who smoke for taking a broad view of research for health; in a population (outcome) discount viagra soft 50mg without prescription erectile dysfunction symptoms, which represents they highlight the value of combining investiga- a risk factor for lung quality viagra soft 50mg lloyds pharmacy erectile dysfunction pills, heart and other diseases tions both within and outside the health sector (impact) order viagra soft with a mastercard erectile dysfunction caused by jelqing, is afected by various services and poli- with the aim of achieving policies for “heath in cies that prevent ill-health and promote good all sectors” (Box 1 purchase generic viagra soft canada erectile dysfunction agents. Among these services and poli- Even with an understanding of the deter- cies are face-to-face counselling, anti-smoking minants and consequences of service coverage, campaigns, bans on smoking in public places, the balancing of investments in health services is and taxes on tobacco products. Te allocation of coverage achieved by these interventions, which public money to health also has ethical, moral and are ofen used in combination, infuences the political implications. Public debate, based on evi- number of smokers in the population (21). Smoking, like many other risk fac- under what conditions, and for what range of ser- tors, tends to be more frequent among those who vices. Decisions on these issues, which involve a have had less formal education and who have combination of ethical imperatives and political 9 Research for universal health coverage Box 1. What do universal health coverage and social protection mean for people afected by tuberculosis? Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease of poverty that drives people deeper into poverty (22). In recognition of this fact, TB diagnosis and treatment are free of charge for patients in most countries. The cost of TB treatment, provided as a public service, is covered by domestic health-care budgets, often supplemented by international grants or loans (23). This helps to reduce the financial barriers to accessing and adhering to treatment. However, free public health services are often not entirely free, and patients always face other expenses. Payments are made for medical tests, medicines, consultation fees and transport, and there are indirect costs of illness due to lost earnings. For patients, therefore, the total cost of an episode of TB is often large in relation to their income (24). The aver- age total cost incurred by TB patients in low- and middle-income countries has been estimated at between 20% and 40% of annual family income, and the relative cost is higher in the lower socioeconomic groups (25–32). The poorest patients become indebted: 40−70% of them according to three studies carried out in Africa and Asia (26, 28, 29). A large part of the cost of TB treatment is incurred during the diagnostic phase before treatment starts in a subsidized TB programme. Costs are especially high for diagnosis and treatment by private doctors, with whom many of the very poorest seek care first (28, 29, 33, 34). Financial costs are commonly compounded by adverse social consequences – such as rejection by family and friends, divorce, expulsion from school and loss of employment – which affect women in particular (35–37). The research behind these findings has been essential for documenting the obstacles to the use of health services and the financial vulnerability of families affected by TB. It has helped to pinpoint where improved services, health insurance coverage and social protection can safeguard against the consequences of potentially fatal and financially catastrophic illness (38). The results have begun to inform national policy on social protection for people with TB (39, 40). Beyond free diagnosis and treatment, a full package of measures for social protection requires the following: ■ Universal health care, free of cost, or heavily subsidized. People do not enter the health-care system as TB patients eligible for free treatment; they typically enter as patients with a respiratory illness.
Buy viagra soft american express. Advanced Erectile Dysfunction Due to Diabetic Neuropathy with an Anonymous Guest.