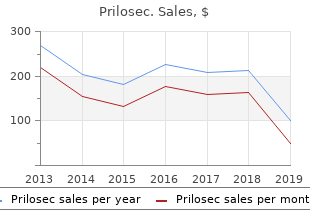
Prilosec
University Centre Doncaster. B. Cyrus, MD: "Purchase Prilosec online no RX. Trusted Prilosec online no RX.".
Depending on the formulation of co-amoxiclav available: Ratio 8:1: 3000 mg/day = 2 tablets of 500/62 buy prilosec master card gastritis diet óķčāåš. If the clinical condition does not improve after 48 hours with ceftriaxone + cloxacillin buy prilosec 20mg low cost gastritis diet x90, consider tuberculosis cheap 10mg prilosec mastercard diet for gastritis and diverticulitis. If tuberculosis is unlikely discount prilosec 20mg free shipping gastritis diet journal, continue with ceftriaxone + cloxacillin and add azithromycin (see atypical pneumonia). Bacteria responsible for atypical pneumonia are mainly Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydophila pneumoniae. Clinical features ā General signs: change in overall condition, pallor, high fever or hypothermia, frequently signs of shock; presence of skin lesions (point of bacterial entry), however, skin lesions may be absent. Pulmonary auscultation is often normal; sometimes dullness indicating pleural effusion. Clinical evolution ā There is a serious risk of decompensation from pneumothorax or suppurative pleurisy or pyopneumothorax. These episodes are usually associated with airflow obstruction within the lung, often reversible, either spontaneously or with treatment. Factors that precipitate/aggravate asthma include: allergens, infection, exercise, drugs (aspirin), tobacco, etc. In young children, most initial episodes of asthma-like symptoms are associated with a respiratory tract infection, with no symptoms between infections. Wheezing episodes usually become less frequent with time; most of these children do not develop asthma. Asthma attack (acute asthma) Asthma attack is a substantial worsening of asthma symptoms. Assessment of the severity of asthma attack The severity of the asthma attack must be rapidly evaluated by the following clinical criteria. In children, use a spacera to ease administration (use face mask in children under 3 years). Single puffs should be given one at a time, let the child breathe 4 to 5 times from the spacer before repeating the procedure. Reassess after 10 days: consider long-term treatment if the asthma attacks have been occurring for several months. If the patient is already receiving long-term treatment, reassess the severity of the asthma (see table page 83) and review compliance and correct use of medication and adjust treatment if necessary. The child breathes from the mouth of the bottle in the same way as he would with a spacer. In mild or moderate asthma attacks, administering oxygen reduces the risk of foetal hypoxia. Chronic asthma Clinical features ā Asthma should be suspected in patients with episodic respiratory symptoms (wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath and/or cough) of variable frequency, severity and duration, disturbing sleep, and causing the patient to sit up to breathe. Patients with typical symptoms of asthma and a history of disease that is characteristic of asthma should be considered as having asthma after exclusion of other diagnoses. The assessment of the frequency of daytime and nigthtime symptoms and limitations of physical activity determines whether asthma is intermittent or persistent. Treatment is started at the step most appropriate to initial severity then, re-evaluated and adjusted according to clinical response.
Groups provide special opportunities for provision of additional social support buy generic prilosec 40 mg online gastritis xantomatosa, interpersonal learning order prilosec mastercard gastritis diet 911, and diffusion of the intensity of transference issues through interaction with other group members and the ther- apists order cheapest prilosec gastritis symptoms anxiety. In addition buy prilosec 10mg otc gastritis ulcer, the presence of other patients provides opportunities for patient-based lim- it-setting and for altruistic interactions in which patients can consolidate their gains in the process of helping others. However, these studies had no true control condition, and the efficacy of the group treatment is unclear, given the complexity of the treatment received. Another small chart review study of an āincest groupā for patients with borderline personality disorder (159) suggested shorter subsequent inpatient stays and fewer outpatient visits for treated patients than for control subjects. A randomized trial (160) involving patients with borderline person- ality disorder showed equivalent results with group versus individual dynamically oriented psy- chotherapy, but the small sample size and high dropout rate make the results inconclusive. This quasi-experimental, nonrandomized study showed that patients with borderline personality disorder discharged from a day program with continuing outpa- tient group therapy (N=12) did better than those who did not have group therapy (N=31). There were, however, important differences between the two compar- ison groups that could account for outcome differences. Perhaps the most interesting aspect of group therapy is the use of groups to consolidate and maintain improvement from the inpatient stay. Linehan and colleagues (8) combined individ- ual and group therapy, making the specific effect of the group component unclear. They re- ported that, contrary to expectations, the addition of group skills training to individual dialectical behavior therapy did not improve clinical outcome. Such groups provide a milieu in which their current emotional reactions and self-defeating behaviors can be seen and understood. Groups may also provide a context in which patients may initiate healthy risk-taking in relationships. Group treatment has also been included in studies of psychodynamic psychotherapy; although the overall treatment program was effective, the effectiveness of the group therapy component is unknown (9, 162). Clinical wisdom indicates for many patients combined group and individual psychotherapy is more effective than either treatment alone. Marziali and Monroe-Blum (163) calculated that group psy- chotherapy for borderline personality disorder costs about one-sixth as much as individual psychotherapy, assuming that the fee for individual therapy is only slightly higher than that for group therapy. However, this potential saving is tempered by the fact that most treatment reg- imens for borderline personality disorder combine group interventions with individual therapy. Treatment of Patients With Borderline Personality Disorder 53 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. In some studies, groups are time-limitedāfor example, 12 weekly sessionsāwhereas in other studies they continue for a year or more. Other po- tential risks of treating patients with borderline personality disorder in group settings include shared resistance to therapeutic work, hostile or other destructive interactions among patients, intensification of transference problems, and symptom ācontagion. Patients in group therapy must agree to con- fidentiality regarding the information shared by other patients and to clear guidelines regarding contact with other members outside the group setting. It is critical that there be no āsecretsā and that all interactions among group members be discussed in the group, especially informa- tion regarding threats of harm to self or others. Couples therapy a) Goals The usual goal of couples therapy is to stabilize and strengthen the relationship between the partners or to clarify the nonviability of the relationship. An alternative or additional goal for some is to educate and clarify for the spouse or partner of the patient with borderline person- ality disorder the process that is taking place within the relationship. Partners of patients with borderline personality disorder may struggle to accommodate the patientās alternating patterns of idealization and depreciation as well as other interpersonal behaviors. As a result, spouses may become dysphoric and self-doubting; they may also become overly attentive and exhibit reaction formation. The goal of treatment is to explore and change these maladaptive reactions and problematic interactions between partners.
Depending on the type of substance discount 40mg prilosec with visa gastritis symptoms throat, alertness and perception are affected prilosec 40mg cheap gastritis ulcer disease, impulsiveness is stimulated buy prilosec 10 mg online gastritis symptoms bleeding, reaction times are slowing order prilosec 10mg fast delivery gastritis keeping me up at night, etc. Moreover, the relationship between concentrations of drugs and driver performance is difficult to establish (Berning, Compton & Wochinger, 2015). The role of medicines in road accidents is not clear as they can influence the capacity of driving positively or negatively (on the one hand they suppress or mitigate the manifestations of an illness, on the other hand they may have undesirable side effects). If a driver is under the influence of a combination of alcohol and drugs, the risk of being involved in crashes further increases. Changing public attitudes towards drink-driving, the adoption of legal measures and enhanced enforcement have certainly contributed to the decrease of road deaths attributed to alcohol. Thanks to these projects, it is possible to study and compare the opinions and attitudes and reported behaviour of the road users in different countries. The subjects covered a range of subjects, including the attitudes towards unsafe traffic behaviour, self-declared (unsafe) behaviour in traffic, and support for road safety policy measures ā overall over 222 variables. A Belgian polling agency coordinated the field work to guarantee a uniform sampling procedure and methodology. The results of the 2015 survey are published in a Main report and six thematic reports: ļ· Speeding ļ· Driving under the influence of alcohol and drugs ļ· Distraction and fatigue ļ· Seat belt and child restraint systems ļ· Subjective safety and risk perception ļ· Enforcement and support for road safety policy measures There are also 17 country fact sheets in which the main results per country are compared with an European average. An overview of the data collection method and the sample per country can be found in the Main report. The present thematic report on driving under influence of alcohol and drugs embraces the following questions: Where you live, how acceptable would most other people say it is for a driver toā¦.? In order to assess if the answers were significantly different from one group to another (for example men vs. Part two (further analyses) consists of inferential statistics (logistic regression models describing the relationship between several explanatory variables such as gender, age, level of education, driving frequency, attitudes towards impaired driving, support of measures, acceptability of impaired driving, risk perception and the binary dependent variable āpresence or absence of self-reported drink-driving, respectively self-reported drug-drivingā). Descriptive analysis The first part of this chapter (descriptive analysis) focuses on the attitudes and opinions towards drink-driving, resp. The acceptability of such behaviours and the opinion about the risks related to these behaviours are analysed in detail. In the second part of this chapter, the analyses will concentrate on self-reported driving under the influence of an impairing substance, including medication. Acceptability of impaired driving (other people and personally) Two similar questions were asked in order to find out the level of acceptability of the behaviour ādriving under the influence of an impairing substanceā: ļ· āWhere you live, how acceptable would most other people say it is for a driver to drive under the influence of.? A large majority of the respondents (about 97%) were of the opinion that driving under the influence of an impairing substance is unacceptable, rather unacceptable or were neutral (scores 1 to 3) and only 3. Most of the respondents seem to believe that other people somewhat find these behaviours more acceptable than they do: the percentages of persons answering that āothersā find it acceptable to drive under the influence of an impairing substance ranged between 5. The level of acceptability of the three behaviours ādrink-drivingā, ādrug-drivingā and ādrink-drug-drivingā is very close. Drink-driving seems to be a little bit more acceptable than driving under the influence of both alcohol and drugs. In all countries, the same phenomenon can be observed: the respondents consider that other people somewhat more readily accept drink-driving or drug-driving than they do themselves. The āperceived social acceptability ratesā on this matter are the lowest in the same two countries where the level of personal acceptability was the smallest (1. The countries with the lowest and highest acceptability (perceived social as well as personal) rates for ādrink-drivingā also have the lowest and highest acceptability rates for drink-drug-driving. An exception is the country with the second highest personal acceptability rate: Poland in place of France. The acceptability rate of drug-driving by country reveals an interesting fact: the country with the maximum respondents indicating that it is acceptable to start driving 1 hour after using drugs (other than medication) is Finland, whereas it has one of the lowest acceptability rate for drink-driving (see also point 4 Discussion. The country with the second highest personal acceptability rate of drug- driving is Italy (4.
Infect Dis Obstet intraepithelial neoplasia: natural history and effects of treatment Gynecol 2011 buy prilosec mastercard gastritis or pancreatitis;2011:806105 cheap prilosec 20mg with visa gastritis on ct. Imiquimod 5% cream induced background and consensus recommendations from the College of psoriasis: a case report best prilosec 20 mg gastritis zeludac, summary of the literature and mechanism discount prilosec 40 mg with mastercard gastritis diet coke. American Pathologists and the American Society for Colposcopy and Br J Dermatol 2011;164:670-2. Use of the cytobrush for Papanicolaou smear order on Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae test screens in pregnant women. J Natl after hysterectomy for reasons other than malignancy: a systematic Cancer Inst 2009;101:1120ā30. European guidelines for quality colposcopy, and human papillomavirus testing in adolescents. J Adolesc assurance in cervical cancer screening: recommendations for collecting Health 2008;43(4 Suppl):S41ā51. The psychosocial impact of and human papillomavirus testing in anal cancer screening. Pap smear versus A epidemiology in the United States-implications for vaccination speculum examination: can we teach providers to educate patients? Long-term immunogenicity triage methods for the management of borderline abnormal cervical of hepatitis A virus vaccine in Alaska 17 years after initial childhood smears: an open randomised trial. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus for the management of women with abnormal cervical cancer screening infection. European guideline for the management of estimate global hepatitis B disease burden and vaccination impact. Lindane toxicity: a comprehensive review transmission of hepatitis B virus in a rural district in Ghana. Curr Opin efficacy 24 years after the start of hepatitis B vaccination in two Gambian Infect Dis 2010;23:111ā8. Etiology of clinical proctitis among evaluation of the efficacy of fewer than three doses of a bivalent men who have sex with men. Permethrin-resistant human exposures to human immunodeficiency virus and recommendations head lice, Pediculus capitis, and their treatment. Prevalence of human use among Ontario female adolescent sexual assault victims: a papillomavirus in the oral cavity/oropharynx in a large population of prospective analysis. Prospective cohort study of detection of Trichomonas vaginalis in urine specimens. Child sexual abuse, links to later sexual transmitted infections in suspected child victims of sexual assault. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents Trichomonas vaginalis: a case report. Postexposure prophylaxis in children and adolescents for transmission of Chlamydia trachomatis. Paper copy subscriptions are available through the Superintendent of Documents, U. Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.
Order 20mg prilosec with mastercard. Sean Evans Answers Fans Questions | Hot Ones.