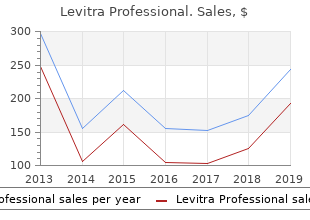
Levitra Professional
Sherwood Psychotherapy Training Institute. X. Ugo, MD: "Buy Levitra Professional. Proven Levitra Professional online no RX.".
None of the investigators have any affiliations or financial involvement that conflicts with the material presented in this report buy levitra professional 20 mg erectile dysfunction doctor dc. The information in this report is intended to help health care decisionmakers—patients and clinicians discount levitra professional 20 mg visa doctor for erectile dysfunction in ahmedabad, health system leaders purchase 20mg levitra professional free shipping female erectile dysfunction drugs, and policymakers cheap levitra professional 20mg free shipping erectile dysfunction doctors in sri lanka, among others—make well-informed decisions and thereby improve the quality of health care services. This report is not intended to be a substitute for the application of clinical judgment. Anyone who makes decisions concerning the provision of clinical care should consider this report in the same way as any medical reference and in conjunction with all other pertinent information, i. This report is made available to the public under the terms of a licensing agreement between the author and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. This report may be used and reprinted without permission except those copyrighted materials that are clearly noted in the report. Further reproduction of those copyrighted materials is prohibited without the express permission of copyright holders. Department of Health and Human Services endorsement of any derivative products that may be developed from this report, such as clinical practice guidelines, other quality enhancement tools, or reimbursement or coverage policies, may not be stated or implied. If an assessment is done, the resulting surveillance report describing the methodology and findings will be found on the Effective Health Care Program Web site at www. Persons using assistive technology may not be able to fully access information in this report. Improving Antibiotic Prescribing for Uncomplicated Acute Respiratory Tract Infections. These reviews provide comprehensive, science-based information on common, costly medical conditions, and new health care technologies and strategies. Systematic reviews are the building blocks underlying evidence-based practice; they focus attention on the strength and limits of evidence from research studies about the effectiveness and safety of a clinical intervention. In the context of developing recommendations for practice, systematic reviews can help clarify whether assertions about the value of the intervention are based on strong evidence from clinical studies. Transparency and stakeholder input are essential to the Effective Health Care Program. Director Director Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Center for Evidence and Practice Improvement Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Stephanie Chang, M. Director Task Order Officer Evidence-based Practice Center Program Center for Evidence and Practice Improvement Center for Evidence and Practice Improvement Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality iii Acknowledgmentsthe authors gratefully acknowledge the following individuals for their contributions to this project: Leah Williams, B. Key Informants are not involved in the analysis of the evidence or the writing of the report. Therefore, in the end, study questions, design, methodological approaches, and/or conclusions do not necessarily represent the views of individual Key Informants. Key Informants must disclose any financial conflicts of interest greater than $10,000 and any other relevant business or professional conflicts of interest. Because of their role as end-users, individuals with potential conflicts may be retained. The list of Key Informants who participated in developing this report follows: Beth Bolick, D. Divergent and conflicted opinions are common and perceived as healthy scientific discourse that results in a thoughtful, relevant systematic review.
Does the comparative effectiveness differ according to various background contextual factors purchase cheapest levitra professional and levitra professional impotence and diabetes 2, such as the time of year generic 20mg levitra professional with amex erectile dysfunction causes infertility, known patterns of disease activity (e order levitra professional 20mg mastercard doctor for erectile dysfunction in chennai. The analytic framework below (Figure A) illustrates the population buy levitra professional 20 mg low price erectile dysfunction doctor nashville, interventions, outcomes, and adverse effects that guided the literature search and synthesis, and their relationship to the Key Questions. Specific details regarding patient population, intervention components, and outcomes are provided in the next section. Literature searches were updated while the draft report was posted for peer review and public comment in February 2015. Studies identified through the update searches were assessed using the same process of dual review as used for studies identified during the initial searches. Pertinent new literature meeting inclusion criteria was incorporated before the final submission of the report. Studies published in other languages but otherwise appearing to be eligible based on the title or English-language abstract were identified and reviewed in order to evaluate potential language bias. Groups whose attendance policies may indirectly affect the use of antibiotics, such as employers or school officials. We grouped interventions by their components into the following five categories: • Educational/behavioral interventions for clinicians, patients, or both. Any point-of-care tests that are available and used in primary care settings for diagnostic purposes with the ability to provide results within a reasonable period of time were included, such as inflammatory tests (e. Key Question 6 Adverse effects of the strategy, such as increased time burden on clinicians, sustainability of intervention, diagnostic resource use, diagnostic coding shifts. Setting Outpatient care settings, including institutional settings, emergency care settings, and other settings, such as school or workplace. Study Designs Systematic reviews with similar scope and search dates within past 3 years. For areas in which such direct comparative evidence is lacking, before-after studies that used methods to control for potential confounding and studies with a time-series design that evaluated temporal trends. Abstracts for citations identified through searches were screened for eligibility by one reviewer, with any deemed ineligible checked by a second reviewer. Full text of all citations deemed potentially eligible for inclusion by at least one reviewer was obtained for further evaluation by two reviewers, with differences in judgment on eligibility resolved through consensus or inclusion of a third party. Data Extraction Study characteristics and results were abstracted from included studies. One reviewer abstracted study data and a second reviewer appraised the abstractions. We considered potential effect modifiers or sources of heterogeneity, which are listed in Table B. All assessments were done at the overall study level and resulted in a rating of good, fair, or poor. We used a dual rating procedure for study quality in which all studies were first rated by one reviewer and then checked by another reviewer. Data Synthesis We used a hierarchy-of-evidence approach that focused on the best evidence for each question, organized into the five intervention categories shown previously (Table A). We synthesized outcome data quantitatively using meta-analysis to pool outcomes where appropriate. When meta-analysis was not suitable because of significant heterogeneity in design, patient population, interventions, and outcomes, we synthesized the evidence qualitatively by grouping studies by similarity of population and/or intervention characteristics, including the sources of variation or heterogeneity listed in Table B. For this project, one of the primary outcomes that Key Informants were interested in was improved appropriate antibiotic use. However, most studies did not measure outcomes in this way, and the few studies that attempted to assess appropriate prescribing had important limitations in outcome definition and ascertainment methods, and lack of consistency in methods across studies. Similarly, very few studies measured actual use of prescribed antibiotics, and even fewer studies reported antibiotic resistance as an outcome.
In contrast purchase line levitra professional erectile dysfunction diabetes cure, a trial using an internet-based training module reported a mean time of 37 buy levitra professional line erectile dysfunction over the counter drugs. The single trial that targeted the parents of pediatric patients 41 required seven minutes of participant time safe 20 mg levitra professional erectile dysfunction pills not working. Although these are real concerns for the feasibility of such communication training interventions purchase generic levitra professional line impotence stress, at least one trial recognized the potential counter-balancing benefit of providing 87 continuing medical education credit for participating clinicians. Another trial found that the effect of communication training on antibiotic prescribing may extend for several years, suggesting that a long-term benefit of such interventions may counter balance the time required 57 56 up front. Conversely, the single poor-quality trial found that the rate of antibiotic prescription among clinicians who received communication training, which decreased at 6 weeks after the intervention (from 36. Clinical Interventions Delayed Prescribing Strategiesthe studies of clinical strategies did not specifically measure or report on increased time burden on clinicians, sustainability of intervention (e. Compared with issuing an immediate antibiotic prescription, conceivably there is at least some increase in time burden for clinicians using delayed prescribing strategies in (1) getting oriented to using a new prescribing approach, (2) explaining to patients the likely natural history of their illness and that it would probably not be helped by antibiotics, (3) providing instructions on how to decide if and when to use the prescription, and (4) fielding patients’ related questions. For example, one study provided the standardized script that clinicians were asked to use when issuing a delayed prescription, which was 235 words in length and would likely require a few minutes to read to their 133 patients. Delayed antibiotic prescription strategies requiring recontact would also require increased time for clinicians and patients compared with immediate antibiotics or delayed antibiotic strategies in which the prescription was given at the time of the visit with instructions 92 to delay or with postdating. Delayed strategies requiring the patient to return for collection of 92 the prescription would also require more patient time. For standardized decision rules, although there would likely be an initial time investment for clinicians in getting oriented to its use, how the time burden of its implementation would compare to that of the usual care process of deciding whether immediate antibiotics are needed would likely vary based on the complexity of the decision rule. For example, the sore throat decision rule utilized in the single relevant study we identified, was very simple, only including scoring of four objective indicators (e. Four trials described the amount of 56,58,80,95 time the various interventions required of the participants. One trial used an intervention with an internet-based training module (mean time 26. Procalcitonin Point-of-Care Testingthe five trials and two reviews of procalcitonin did not specifically measure or report on increased time burden on clinicians, sustainability of intervention (e. The studies reported a range of 1 to 4 hours for test results being reported to the clinician, depending on where and how it was processed and reported. In all studies, clinicians communicated with patients via telephone to provide instructions on antibiotic use following interpretation of the test result. In some the patients had all been given a prescription and asked to not fill it until they heard from the clinician. Those who were deemed to not need an antibiotic were asked to return the prescription by mail. While these procedures may have been study related, they do raise questions about what process is used for handling prescribing decisions when the decision is delayed until after the patient is no longer in the clinic. System-Level Interventions While none of the system-level intervention studies explicitly addressed potential adverse effects of implementing the interventions or reported on the time burden associated with developing, deploying or using them, one study reported a decrease in ordering in rapid 103 streptococcal tests associated with their system-level intervention. There was no difference in the proportion of physicians in the intervention versus control groups ordering chest radiographs however (21. Multifaceted Interventions No study using multiple interventions explicitly measured adverse consequences of the time burden used to create and implement the intervention, although some discussed dropout rates and participation rates, which may be related. Seven studies described the amount of time required by participants to engage in the intervention, undergo training sessions, or participate in site visits or 41,79,102,129,146,147,154,167,168 workshops.
Professional typists were asked to type with the same visual behavior and they could not type words order levitra professional 20mg free shipping erectile dysfunction in young males. The scientists noticed that every facilitator however stared intently at the keyboard order levitra professional 20 mg on line erectile dysfunction zinc supplements. In This study the autistic child was shown a picture of an object purchase 20 mg levitra professional with visa erectile dysfunction drugs reviews, then the facilitator was shown a different picture cheap levitra professional 20 mg on-line erectile dysfunction va disability rating. Frontline broadcasts a set of keys shown to the child and some tennis shoes shown to the facilitator. Hundreds of studies are performed in a variety of ways to find out from whose conscious ness is the words coming from. But this is not the first or the last case of subtle muscle control resulting in a cult therapy. Both of these techniques depend on the subtle interface of the facilitator or the therapist on the patient. Pendulums, Ouija boards, fingers sticking to radionic rub plates, finger modes, and many others are used throughout history to express the unconscious. The unconscious can express itself through this subtle interaction as we can see from research in autonomic functions. The right brain is wired to the autonomic system more distinctly than the more conscious left brain. To use this divination to express our unconscious is one thing, but to promote it as science and accept its results as true evidence of disease is clearly another. The tester cannot function if his measurement techniques do not allow contact of the subtle muscles with the patient. He discovered that the acupuncture points had different skin resistance from the surrounding skin. By using a type of simple skin resistance device he could measure the resistance and compare it to norms. Attempts to confirm the medication testing effect with just resistance devices on the skin were futile. Vol rationalized that the circuit needed to be broken for the effect to work but even breaking the circuit with machines did not work. The unconscious of therapist controls the result not the changes in patient as is the claim. The subtle action of the "speed of the probe contact" is the primary determinant of the reading. If the probe is pushed in quickly a high reading results, if slowly a lower reading results. Factors of end pressure and twisting of the probe also contribute to the facilitation or subtle control of the therapist. The therapist tests vitamins, minerals and other supplements on a test tray or computer screen. By seeing what he tests the therapist’s unconscious controls the subtlety of the probe-patient contact and thus determines the result. If the we turn off the screen or double blind the therapist from knowing what is being tested the therapist is lost and frustrated. Certain Kinesiologists thought that they could test the reaction of a patient to supplements with their muscle testing. By placing the supplement on the patient they then challenge a muscle with pressure before and after and compare results. If we apply a gauge to the therapist to measure his pressure, such as a rubber band with consistent length, a scale of consistent pressure, or a pressure measuring device we can easily see that the therapist applies a wide variety of pressures.
Purchase cheap levitra professional on line. Erectile dysfunction can be treated by Aloevera.